High Intake of Junk Food and Antacids Causes 1,500 Gallbladder Stones in Woman
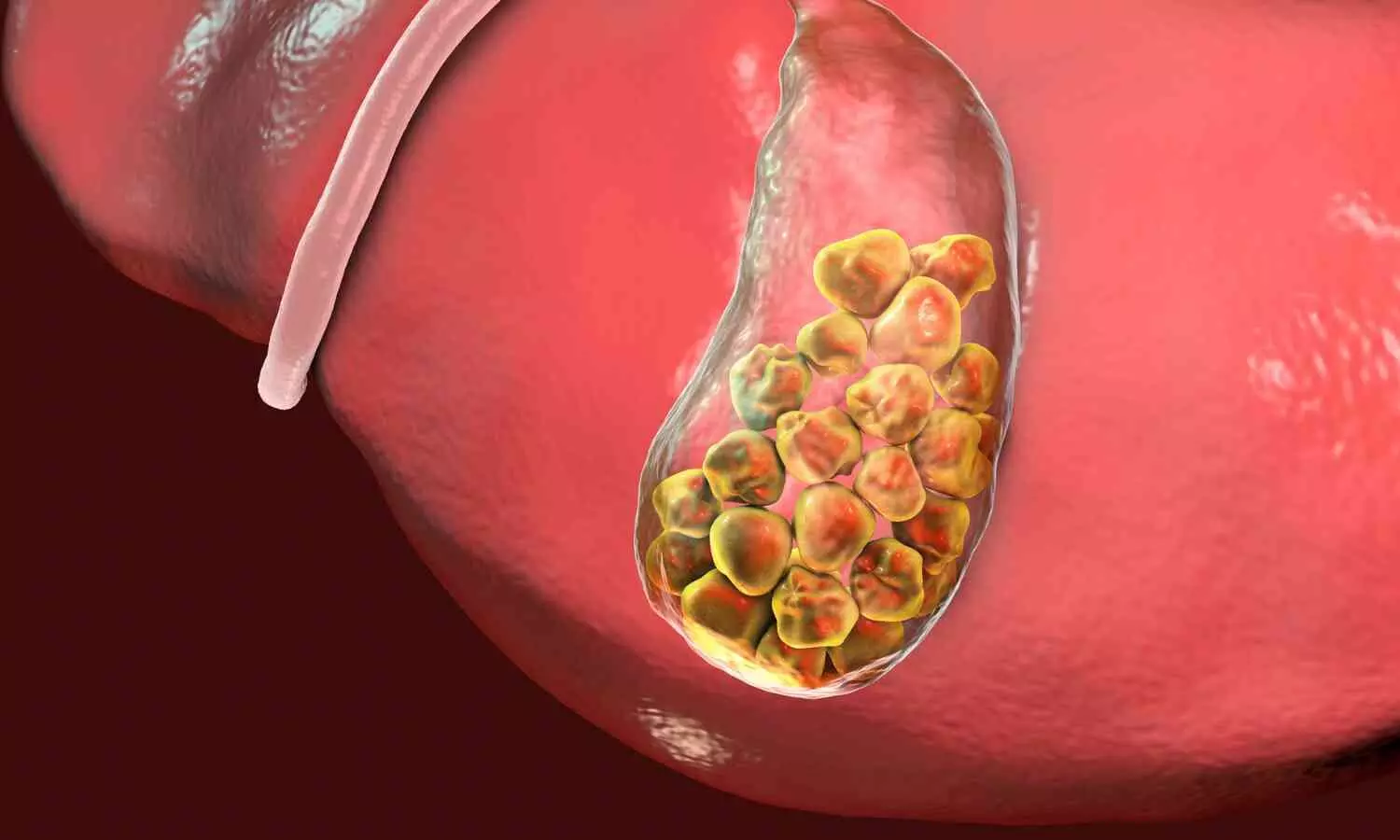
New Delhi: In a shocking medical case, doctors at Sir Ganga Ram Hospital successfully removed 1,500 stones from the gallbladder of a 32-year-old woman.
The patient, an IT professional, had a diet high in junk and fatty foods which led to bloating, distension, and a feeling of heaviness. To manage these symptoms, she frequently took over-the-counter (OTC) antacids for the past three to four months. Additionally, she experienced recurrent pain in her right upper abdomen, which radiated to her back and right shoulder, often accompanied by nausea and vomiting.
Upon consulting her family physician, an ultrasound was recommended, revealing her gallbladder was filled with stones. Consequently, doctors at Sir Ganga Ram Hospital advised keyhole surgery, also known as Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy, to remove the gallbladder along with the stones.
The surgical team, led by Dr. Manish K. Gupta, Vice Chairperson and Senior Consultant, Laparoscopic & General Surgeon, performed the procedure by making 10mm and 5mm incisions in her abdomen.
“It was surprising to find out that the gallbladder was full of multiple large and small stones, numbering almost more than 1,500,” Dr. Gupta said.
Dr. Gupta noted that lifestyle changes, prolonged gaps between meals, and extended fasting periods leading to bile precipitation are contributing to the rising incidence of gallstones in the country.
“Even small stones can slip into the Common Bile Duct (CBD) and cause jaundice or pancreatitis. Large stones, if left untreated in the gallbladder for a very long time, can predispose to cancer of the gallbladder due to chronic irritation,” he explained.
The patient was discharged the day after surgery and was able to eat a normal diet and move around independently.
This case highlights the growing prevalence of gallstones due to lifestyle factors and underscores the importance of early diagnosis and timely surgical intervention to prevent severe complications such as jaundice, pancreatitis, and gallbladder cancer.
Gallstones, or cholelithiasis, form in the gallbladder due to various factors. Primarily, they develop when there's an imbalance in the substances that make up bile, such as cholesterol, bile salts, and bilirubin. High cholesterol levels in the bile can lead to the formation of cholesterol stones, while excessive bilirubin can result in pigment stones. Sir Ganga Ram Hospital continues to lead in providing advanced medical care and surgical solutions, ensuring quick recovery and improved quality of life for patients.


