Global Handgrip Strength Norms Established: Insights from a Study of 2.4 Million Adults
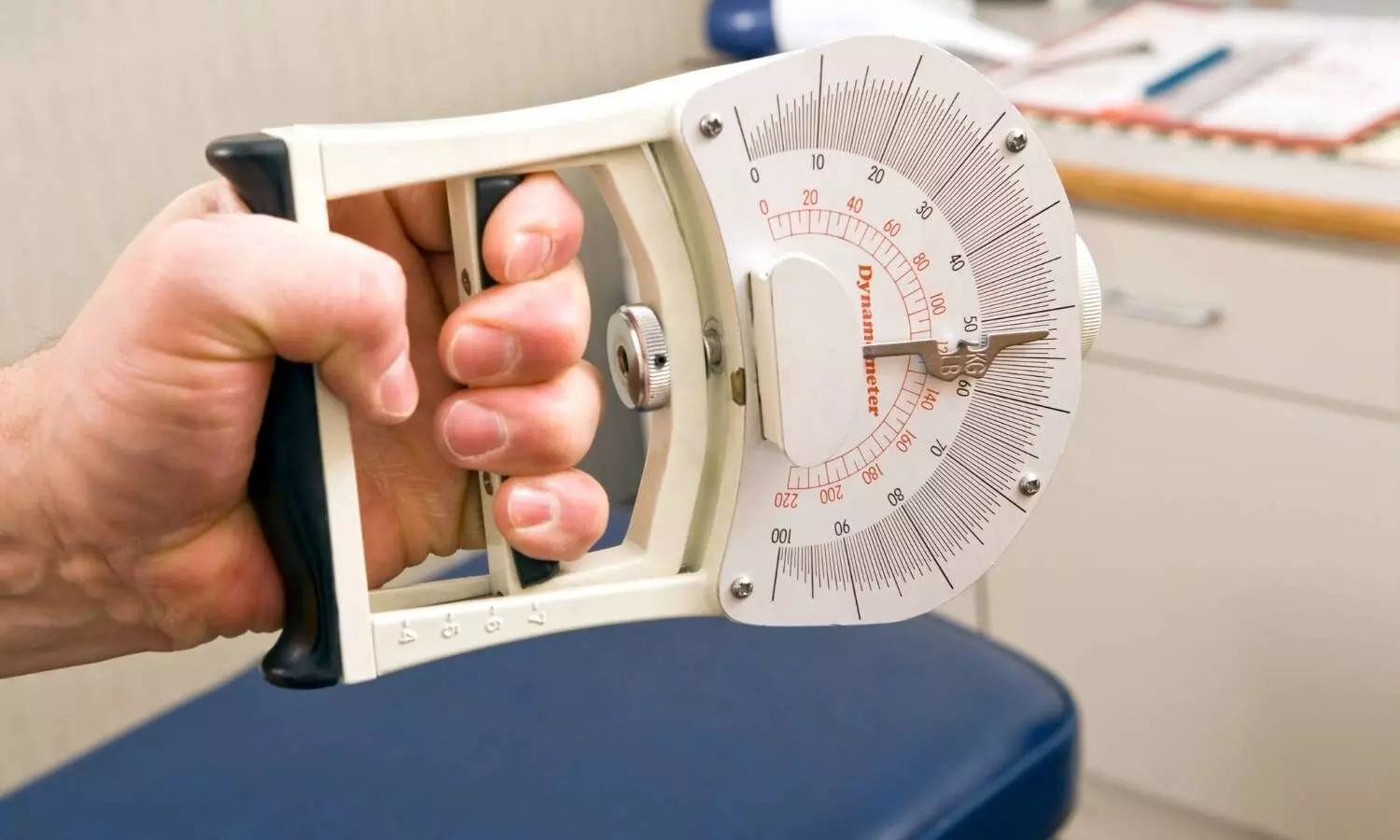
New Delhi: A recent study published in the Journal of Sport and Health Science has established comprehensive international norms for adult handgrip strength (HGS), a key indicator of overall health and physical capability. The study found that HGS peaks between ages 30–39, averaging 47.8 kg for men and 29.7 kg for women, before gradually declining with age. This age-related decline accelerates in later adulthood, underscoring the importance of maintaining muscular strength throughout life.
The findings are based on data from 2.4 million adults aged 20 to 100+ years, spanning 69 countries. Handgrip strength, measured using isometric dynamometry, is widely recognized as a reliable and feasible method of assessing muscular strength across all age groups.
“Muscular strength is a powerful marker of current health status and a robust predictor of age-related disease and disability,” the authors wrote. “Handgrip strength is a convenient, feasible, and widely used method of assessing muscular strength among people of all ages.”
The study also examined gender differences, showing that men generally have higher handgrip strength than women across all ages. However, this gap narrows slightly as individuals age. Researchers emphasized the clinical significance of handgrip strength, noting its strong correlation with mortality and other health outcomes.
“Low muscular strength better predicts all-cause and cardiovascular mortality than traditional risk factors like systolic blood pressure,” the authors stated. This makes handgrip strength a vital screening tool in clinical and public health settings.
The researchers developed percentile-based benchmarks for both absolute and body-size-normalized HGS, offering a valuable tool for global comparisons and individual health assessments. These benchmarks can help identify individuals at risk of poor health due to low muscular strength and guide targeted interventions.
“These norms have utility for global peer-comparisons, health screening, and surveillance,” the researchers noted. By setting a global standard, the study provides an essential resource for clinicians, policymakers, and researchers working to improve population health and physical fitness worldwide.
“This study provides the world’s largest and most geographically comprehensive international norms for adult HGS by sex and age,” the authors concluded.
This research highlights the importance of muscular strength as a key health metric and its potential to inform global health policies and interventions.


