Healing with Cold: What to Know About Cryoablation - Dr Abhishek Bansal
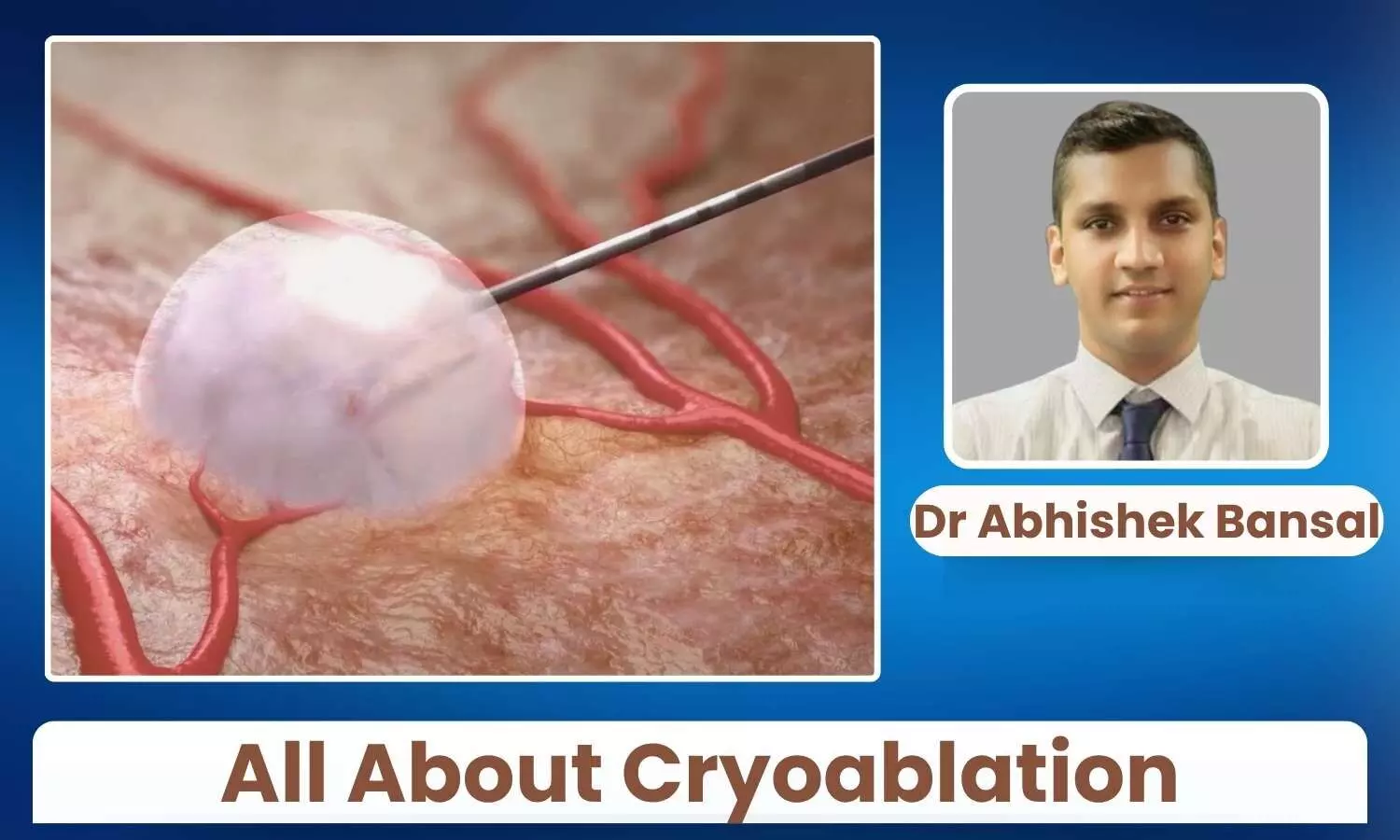
As cancer rates continue to rise globally, innovative treatments like cryoablation are offering new hope, freezing tumours with precision and minimizing damage to healthy tissue.
In 2022, approximately 2 crore new cancer cases were diagnosed worldwide, with 97 lakh deaths, and projections indicate that new cases may soar to about 3.5 crore by 2050 due to population growth, ageing, and rising exposure to risk factors like tobacco, alcohol, obesity, and pollution.
India recorded around 14 lakh new cases and 917,000 deaths in 2022, with breast, oral, cervical, lung, and esophageal cancers leading the tally, driven largely by tobacco use, lifestyle changes, and environmental hazard. According to the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), the estimated number of incidences of cancer cases was more than 14 lakhs in 2023 in India.
Considering the current cancer burden in India and the evolving landscape of cancer care, cryoablation is emerging as a minimally invasive alternative that harnesses extreme cold to target tumours effectively and with lesser side effects compared to the other available treatment.
What is Cryoablation and How does it work?
Cryoablation is one of the advanced minimally invasive procedures of the present-day healthcare, presenting patients with an option to conventional surgical options. It utilizes extreme cold to destroy abnormal tissues and tumours in the body, specifically in organs like the liver, kidney, lungs, bone, prostate and breast.
The technology of cryoablation involves a temperature drop, the water inside the cells freezes, shattering cell membranes and causing irreversible damage to the affected cells. Physically, multiple cycles of freezing and thawing are applied to the targeted tissue to ensure complete treatment of the affected area.
In the process, doctors use imaging guidance such as CT, USG (ultrasound guidance), or MRI to accurately position a thin cryo probe right into the targeted tissue. The non-surgical procedure involves super cooled argon gas or liquid nitrogen, which quickly converts the affected area into a cooled ice field.
Growing Preference for Cryoablation
Cryoablation provides rapid recovery because it is less physically demanding on the body, patients recover more rapidly, feel less discomfort following treatment, and stay in the hospital for fewer days as compared to conventional treatment options
- Faster Recovery - Quicker recuperation. The surgery is less physically taxing, patients recover faster, experience less discomfort after the procedure, and stay in the hospital for shorter periods, allowing them to resume their regular lives sooner.
- Minimal Scarring - Minimal or no scarring results from needle entry point application, which is a factor of particular importance when thinking about cosmetically sensitive areas like the skin or the breast.
- High Accuracy - Physicians also appreciate cryoablation for its accuracy. When treating tumours that are close to vital organs or structures like blood vessels or nerves, the procedure enables doctors to cure the tumours with a high degree of accuracy while preserving the good tissue in the vicinity.
- Safe for High-Risk Patients - For individuals who might not be able to tolerate traditional surgery because of their advanced age, underlying medical conditions, or previous radiation therapy, cryoablation is a viable alternative.
This innovative freezing treatment is transforming cancer care, making effective treatment possible for more patients while reducing the physical and emotional burden of cancer therapy.
What Type of Cancers can be treated by Cryoablation?
- Lung cancer: In the case of patients who are not candidates for surgery or radiation, cryoablation can specifically treat small lung tumours without destroying surrounding lung tissue, achieving symptom control and disease management.
- Prostate cancer: The treatment is used to treat localized prostate cancer by freezing the whole gland or the injured area.
- Bone cancer: The treatment is used to manage localized bone cancer by freezing the tumour or the involved portion of the bone.
- Breast cancer: Cryoablation is often used for small, early-stage breast cancers, particularly in women who do not want to go ahead with surgery or preserve breast appearance.
- Kidney cancer: For small renal tumours, especially in candidates who are not ideal for surgery, cryoablation ensures good tumours control with maintenance of global kidney function.
- Liver cancer: Cryoablation is used to treat both primary liver cancers (hepatocellular carcinoma) and metastatic tumours from other organs.


